Phototype is a property of the skin determined by the content of melanin in it. Due to the different levels of melanin, a natural pigment, the skin of the world's population differs in color and sensitivity to ultraviolet rays of the sun.
It is important for each person to know their skin phototype, since each phototype reacts differently to ultraviolet rays of sunlight. This will allow you to correctly assess the risks of sunburn, photoaging of the skin and developing skin cancer.
There are several classifications, the most common being the Fitzpatrick classification of skin phototypes.
What is skin phototype?
Skin phototype is a genetically determined characteristic that determines the sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet rays and allows us to predict the skin's reaction to exposure, from ultraviolet to near infrared.
Skin phototype does not change with age, as it is an innate characteristic of the skin.
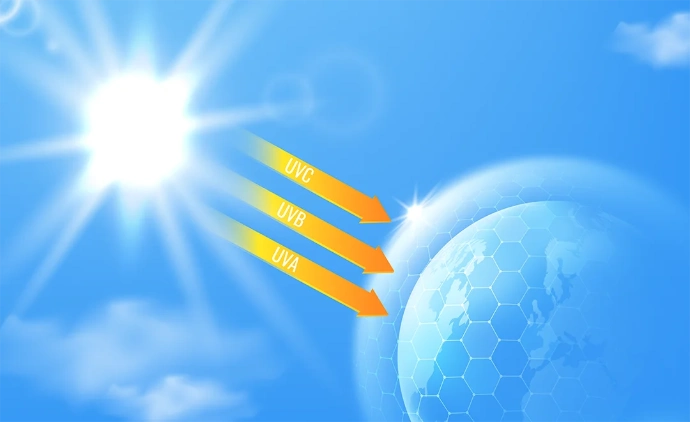
UV rays
Ultraviolet rays are constantly present in solar radiation. They are conventionally divided into 3 ranges. Each range has specific properties and produces different effects on the skin.
Effects of UV rays on the skin
The skin is one of the largest human organs, it performs a protective function and also participates in the metabolism of sex hormones and the synthesis of vitamins.
Vitamin D synthesis
In the skin, under the influence of UVB rays, the active form of vitamin D₃ is formed from dihydrocholesterol. Vitamin D regulates calcium metabolism in the body for the proper formation of the skeleton. If there is a deficiency in childhood, rickets develops. In addition, vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and a tendency to depression.
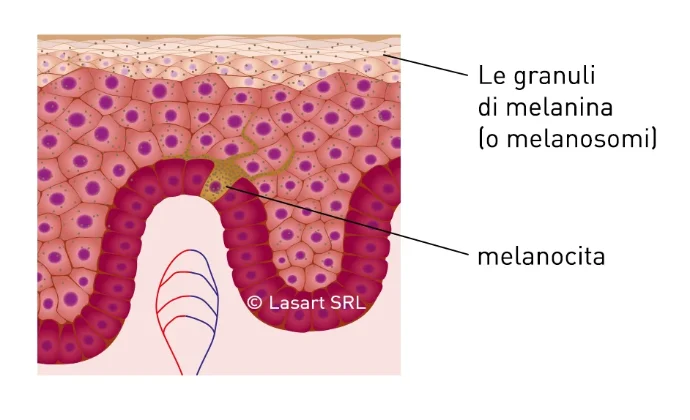
Melanin synthesis and natural skin protection
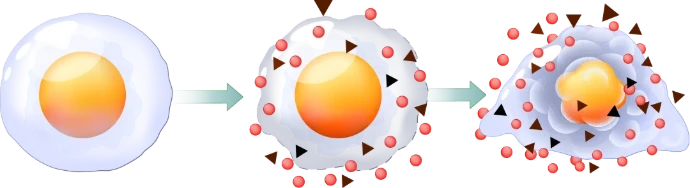
Skin melanin is an important pigment in our body. It is produced by skin cells called melanocytes. The main function of melanin is to absorb dangerous ultraviolet radiation present in sunlight. By absorbing ultraviolet rays, melanin protects the DNA of cells from damage. This is very important because damage to the DNA of skin cells increases the risk of developing skin cancer.
Melanocytes are skin cells that produce melanin, the natural pigment responsible for skin color. By regulating their activity, you can achieve a more even and radiant complexion.
Melanin and pigmentation
Under the influence of ultraviolet rays, our skin tans. Darkening of the skin due to exposure to UV rays is caused by two processes. Rapid changes in skin pigmentation occur due to a chemical reaction of the small amount of melanin present in the skin. Under the influence of ultraviolet light, melanin becomes darker. The second mechanism is slower and is associated with the activation of melanocytes, skin cells that initiate the synthesis of melanin and transport it to the skin cells. This mechanism is longer and takes several days.
Scheme of activation of melanin synthesis by melanocytes and distribution of pigment in the skin
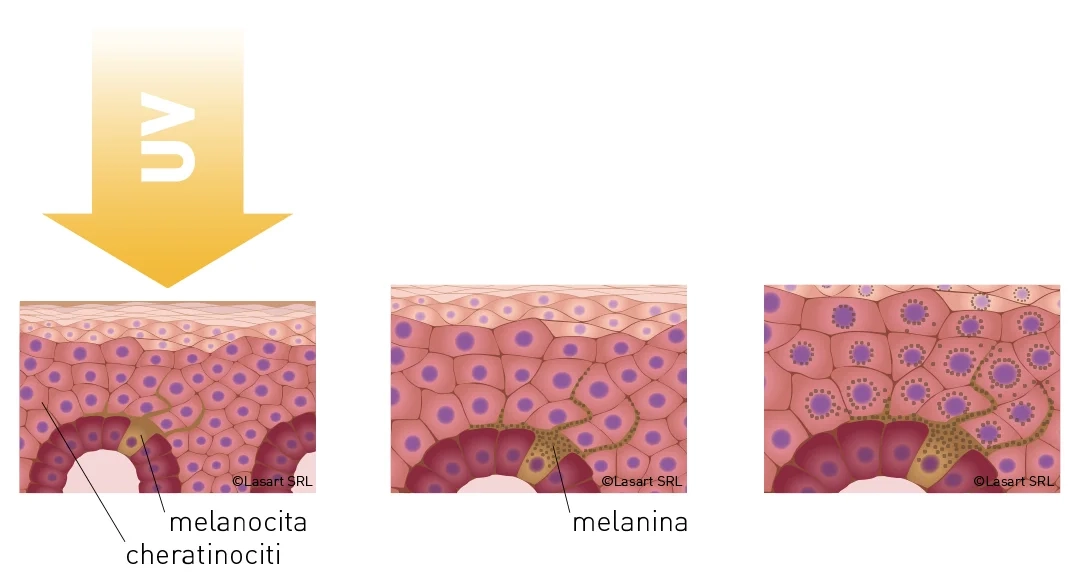
Attivazione dei melanocytes
With increased exposure of the skin to ultraviolet rays, melanocytes are activated.
Melanin synthesis
Melanocytes enhance the synthesis of melanin and transport it to the skin cells: keratinocytes.
Melanin distribution
Melanin spreads throughout the skin cells, forming a "shield" around the cell nucleus and protecting the cells' DNA from damage.
In this way our skin tans and is protected from the negative effects of ultraviolet rays.
Other natural factors that protect the skin from UV rays
In addition to tanning, our skin also has other factors to protect itself from UV rays.
Urocanoic acid is secreted by our skin and is a natural sunscreen with SPF 4. Dry skin becomes more vulnerable, this characteristic is taken into account when we develop our sunscreens thanks to the "Water Shield" technology.
Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation and skin burns, the regeneration of keratinocytes is stimulated, which leads to thickening of the stratum corneum of the skin. Thanks to this, the stratum corneum scatters more ultraviolet radiation and additionally protects the underlying layers of the skin.
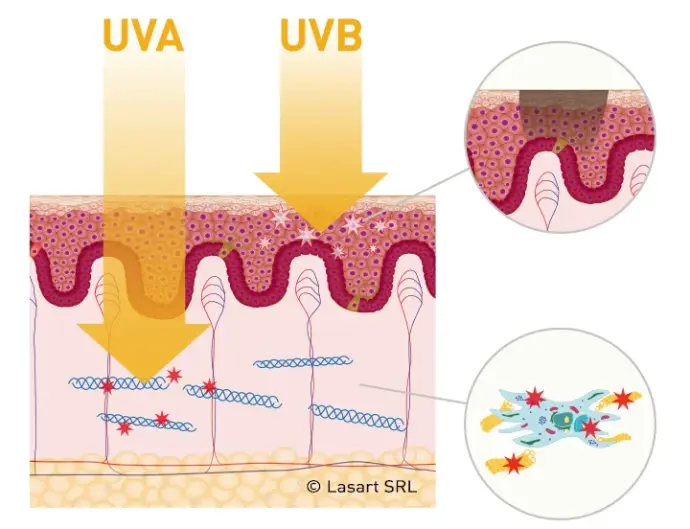
Negative effects of UV rays on the skin
In recent decades, researchers have paid special attention to studying the negative impact of ultraviolet rays on the skin. Depending on the wavelength, UV rays act at different depths, damaging cells and extracellular structures of the skin. The negative effects of UV rays are divided into acute (rapid) and chronic. Rapid effects include sunburn, skin pigmentation, decreased immune defenses, photodermatosis (sun allergy). Chronic effects are cumulative and develop over the years.
105 photodamage of cells caused by UV rays
Each skin cell is exposed to 105 photodamages per day, at varying levels. If the damage is severe, the cells die and the result is a skin burn.
Ultraviolet rays damage cell structures and the DNA of cells. The most dangerous damage is to DNA, which can cause skin cancer.
The depth of penetration of ultraviolet rays into the skin
The depth of penetration of ultraviolet rays into the skin depends on the wavelength. UVB rays penetrate only the surface layer of the skin, the epidermis, to a depth of 100 microns. Ultraviolet rays are able to penetrate the deep layer of the skin, the dermis, which is responsible for the elasticity of our skin. The decrease in collagen in the dermis causes sagging skin and the formation of wrinkles.
What is the meaning of skin phototype?
Historically, at latitudes with high UV intensity (at the equator), the population has a dark complexion. Moving away from the equator, the skin color of the population becomes lighter. Therefore, the human body has adapted to life at latitudes with high UV intensity.

Skin phototypes have gained relevance with the growth of knowledge about the skin. This important indicator is widely used in dermatology to predict the skin's reaction to ultraviolet radiation, to create sunscreens, to determine the parameters of laser procedures, and to develop recommendations for the prevention of skin cancer.
Classification of skin phototypes according to Fitzpatrick
Fitzpatrick's skin phototype classification is based on phenotypic characteristics such as skin and hair color, eye color, and ethnic origin. The classification is used to determine the sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet rays. According to this classification, the population of our planet is divided into 6 skin phototypes.

Phototype 1
Untanned skin is bright white
Blue or green eyes
Freckles are common
Geography of origin: Northern Europe/British.
Phototype 1 has the highest sensitivity to ultraviolet light. It always burns before tanning. The tan is light and disappears quickly when the sun stops.
Daily protection: SPF 30
Risk factors*: SPF 50
*For more information on risk factors, see the section UV Risks and Protection Tips.
Risks for Phototype 1
RISK | |
SUN | maximum risk of sunburn |
CANCER | high |
LASER BURNS | low |
HYPERPIGMENTATION | low risk |
Recommendations for Phototype 1
Extremely limited sun exposure. We recommend using a daily SPF 30 sunscreen on exposed areas of the skin. For added protection, use clothing. If risk factors are present, use a broad-spectrum SPF 50 sunscreen.

Phototype 2
Untanned skin is white
Blue or brown eyes
Red, blonde or brown hair
Geography of origin: Europe, Scandinavia.
Phototype 2 has high sensitivity to ultraviolet light. It often burns before tanning. The tan is light and disappears quickly when the sun stops.
Daily protection: SPF 30
Risk factors*: SPF 50
*For more information on risk factors, see the section UV Risks and Protection Tips.
Risks for Phototype 2
RISK | |
SUN | high risk of sunburn |
CANCER | high |
LASER BURNS | low |
HYPERPIGMENTATION | relatively low |
Recommendations for Phototype 2
Limited sun exposure. It is recommended to use a sunscreen with a minimum protection factor of 30 every day on exposed skin. For additional protection, use clothing. If risk factors are present, use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 50.

Phototype 3
Untanned skin is pale
Brown eyes
Dark hair
Geography of origin: Southern or Central Europe.
Phototype 3 has an average tolerance to UV rays, but still runs the risk of sunburn at the first contact with intense sun. The tan is more intense than phototypes 1 and 2.
Daily protection: SPF 30
Risk factors*: SPF 50
*For more information on risk factors, see the section UV Risks and Protection Tips.
Risks for Phototype 3
RISK | |
SUN | medium risk of sunburn |
CANCER | medium risk of sunburn |
LASER BURNS | medium risk of sunburn |
IPL BURNS | medium-high |
HYPERPIGMENTATION | medium risk of sunburn |
Recommendations for Phototype 3
Although phototype 3 is more adapted to the sun's rays and tans quite quickly, moderate exposure to the sun is still recommended. More attention should be paid to protection from UVA rays, since they have no obvious biological effects. In addition, given the greater resistance to UVB rays, people with phototype 3 can stay in the sun longer, thus increasing the time of exposure to UVA rays. Therefore, despite the higher degree of protection, it is recommended to apply a broad-spectrum protection SPF 30 in the UVA-I and UVA-II range.
The main rule for phototype 3:
prolonged exposure to the sun - apply a sun protection factor >30 with UVA protection.

Phototype 4
The skin light brown skin
Brown eyes
Dark hair
Geography of origin: Mediterranean, Asian or Latin.
Phototype 4 is a phototype that is fairly protected from the sun. People with phototype 4 almost never burn; they tan quickly and intensely.
Daily protection: SPF 30
Risk factors*: SPF 50
*For more information on risk factors, see the section UV Risks and Protection Tips.
Risks for Phototype 4
RISK | |
SUN | Sunburn is extremely rare |
CANCER | medium-low |
LASER BURNS | medium-high |
IPL BURNS | high |
HYPERPIGMENTATION | high |
Recommendations for Phototype 4
IPhototype 4 has skin characteristics similar to phototype 3. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to UVA protection to prevent skin aging.
A characteristic feature of phototype 4 is a high tendency to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Therefore, the risk of hyperpigmentation in patients with phototype 4 during laser procedures is 5 times higher than in patients with phototypes 1 and 2. It is worth keeping this in mind and using SPF 50 sunscreen with UVA-I and UVA-II protection.
The main rule for phototype 4:
if there is inflammation of the skin (acne, procedures) apply SPF 50.

Phototype 5
The skin brown skin
Brown eyes
Dark hair
Geography of Origin: East Indian, Native American, Hispanic, or African.
Phototype 5 tans quickly and is well protected from UVB rays, so the risk of sunburn is minimal. The tan is intense.
Daily protection: SPF 30
Risk factors*: SPF 50
*For more information on risk factors, see the section UV Risks and Protection Tips.
Risks for Phototype 5
RISK | |
SUN | minimum |
CANCER | low |
LASER BURNS | high |
IPL BURNS | procedures are contraindicated |
HYPERPIGMENTATION | high |
Raccomandazioni per Fototipo 5
For phototype 5, it is recommended to use sunscreens to prevent hyperpigmentation. In the presence of long-lasting inflammation (acne, post-procedure), it is recommended to use an SPF 50 with UVA-II and UVA-I protection.
Despite the low risk, prevention of skin cancer and melanoma should also be considered.
The main rule for phototype 5:
if there is inflammation of the skin (acne, procedures) apply SPF 50.

Phototype 6
The skin skin is black
Brown eyes
Dark hair
Geography of origin: African or Aboriginal.
Phototype 6 tans quickly and is well protected from UVB rays, so the risk of sunburn is minimal. The tan is intense.
Daily protection: SPF 30
Risk factors*: SPF 50
*For more information on risk factors, see the section UV Risks and Protection Tips.
Risks for Phototype 6
RISK | |
SUN | minimum |
CANCER | low |
LASER BURNS | high |
IPL BURNS | procedures are contraindicated |
HYPERPIGMENTATION | high |
Recommendations for Phototype 6
For phototype 6 there are no specific recommendations for protecting the skin from the sun.
It is important to remember the prevention of skin cancer and skin photoaging. Risks such as changes in latitude or excursions to the mountains or waterways are not risk factors for phototype 6. However, in case of chronic inflammation, the risk of hyperpigmentation is high.
The main rule for phototype 6:
if there is inflammation of the skin (acne or after procedures) apply SPF 50.
Skin sensitivity to UV rays
The skin has a different sensitivity to ultraviolet rays depending on the phototype. Knowing your phototype allows you to correctly evaluate the risks and avoid the negative effects of UV rays on the skin. People with high phototypes are better protected from the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin.
Skin Phototypes: UV Risks and Protection Tips
Risk of sunburn and skin cancer depending on phototype
The risk of sunburn is highest for phototype I. The skin of people with the first phototype is very sensitive to ultraviolet rays, it almost always burns and tans very poorly. As the phototype increases, the risk of sunburn decreases and people with phototype 6 do not suffer from sunburn. Since the skin of people with phototype 6 is better protected from ultraviolet radiation, they are less likely to develop skin cancer than people with a light phototype.
Melanoma risk
Melanoma is one of the most dangerous types of skin cancer and has a high mortality rate. The risk of skin melanoma is higher in people with light skin types; in addition, living at latitudes close to the equator increases the risk of melanoma. Melanoma is difficult to cure and has a high mortality rate.
Recommendations
It is important to follow the skin protection tips
Get mole screening to detect early stage melanoma
Latitude and altitude in UV exposure
The intensity of UV rays on the globe also varies depending on the geographical area. Don't forget this when you go on a trip.
Prevention from UV rays
UV protection is becoming the norm thanks to the knowledge that is accumulated year after year. The classification of skin phototypes according to Fitzpatrick helps to choose the optimal protection.

Reduce sun exposure
Limit sun exposure between 10am and 4pm
Stick to the shadows
Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun
SPF 30
Broad spectrum UVB + UVA protection. Follow the application instructions. Apply sunscreen to all exposed areas of the body, including hands, décolleté, neck and scalp, where there is no hair..
Clothes and glasses
Wear sun-protective clothing, a wide-brimmed hat, and sunglasses with UV protection.
RECOMMENDATIONS
SPF selection for skin phototypes 1 and 2
Risk factors when it is necessary to increase the level of protection to SPF 50:
- latitude variation closest to the equator;
- trips to the mountains, ski resorts or water places;
- the rehabilitation period in the first 3 months after laser surgery and photorejuvenation on treated skin areas;
- photodermatosis.
Note that. The above information describes the principle of skin protection from UV rays and is advisory in nature. Each person's skin is unique, as is its condition. The choice of sunscreen will depend on this. Follow your doctor's recommendations.
Recommendations for skin types 3 and 4
Skin types 3 and 4 are more protected from ultraviolet rays, tan well and rarely burn. For these skin types, it is sufficient to use an SPF 30 in normal conditions.
People with phototypes 3 and 4 are at greater risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, which is skin pigmentation caused by prolonged inflammation: after acne breakouts, after burns, even after laser procedures.
Unless otherwise prescribed by your doctor, if you have risk factors, follow the recommendations in the table below.
Risk factors for skin hyperpigmentation and recommendations.
Risk factor | Use SPF 50 for |
Acne breakouts with a tendency to pigmentation | until the skin is completely healed and for the next 3 months |
After the skin photorejuvenation procedure | 1-3 months |
Laser or photocoagulation of facial vessels | 3 months |
Laser coagulation of blood vessels on legs and body | 6 months |
Melasma, chloasma | continuous application of SPF |
Remember that SPF does not guarantee 100% skin protection, so do not ignore recommendations for other methods of protection.
Recommendations for skin types 5 and 6
People with phototypes 5 and 6 are better protected from the negative effects of UV rays. They almost never burn and tan quickly. However, if you have risk factors for hyperpigmentation, it is recommended to use an SPF 30 or higher.
Proper sun exposure is the way to healthy, youthful skin
Now you know your phototype and the basic rules to protect your skin from the negative effects of UV rays. Follow these simple rules to reduce the risk of skin cancer and melanoma and keep your skin young and healthy by preventing skin photoaging.
Discover comfort and high protection with Melicor
A line of sunscreens for post-laser surgery and for everyday use.
FAQs
No, skin phototype cannot change with age, since it is a genetically determined property of the skin and is associated with a person's phenotype.
Sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation may vary due to skin and body diseases, as well as in the case of taking photosensitizers.
No, tanning in a solarium does not prevent the negative effects of ultraviolet rays on the skin. On the contrary, exposure to ultraviolet rays from a solarium negatively affects the condition of the skin and increases the risk of skin cancer.
Literature
- D'Orazio, J.; Jarrett, S.; Amaro-Ortiz, A.; Scott, T. UV Radiation and the Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12222-12248.
- Nordlund, J.J. The melanocyte and the epidermal melanin unit: An expanded concept. Dermatol. Clin 2007, 25, 271–281.
- Kawada, A. Risk and preventive factors for skin phototype. J. Dermatol. Sci 2000, 23, S27–S29.
- Holick, M. Does sunscreen block the skin’s ability to make vitamin D? If so, how can I get enough of this vitamin without raising my risk of skin cancer? Health News 2002, 8, 12.
- Hoeijmakers, J. H. DNA damage, aging, and cancer. N. Eng. J. Med 2009 , 361 , 1475–1485.
- Cheyasak N, Manuskiatti W, Maneeprasopchoke P, Wanitphakdeedecha R. Topical corticosteroids minimise the risk of postinflammatory hyper-pigmentation after ablative fractional CO2 laser resurfacing in Asians. Acta Derm Venereol 2015;95:201-5.